1 1/2 Syndrome
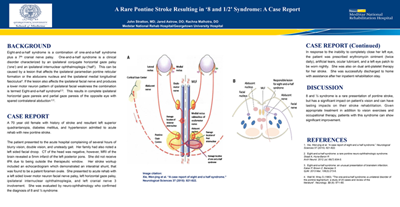
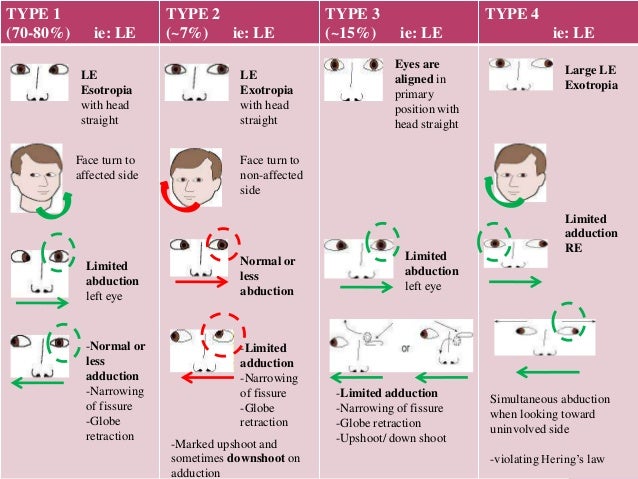
1 1/2 syndrome. One-and-a-half syndrome is a clinical disorder characterized by an ipsilateral conjugate horizontal gaze palsy the one and an ipsilateral internuclear ophthalmoplegia INO the half. The duplication occurs on the long q arm of the chromosome at a location designated q211. In Types 1 2 and 4 Bartters the loss of salt and water into the urine may be severe especially in infants and patients risk becoming dehydrated.
They often come to medical attention because the child doesnt thrive. One-and-a-half syndrome is a disorder of horizontal ocular movement characterized by a lateral gaze palsy on looking toward the side of the lesion and INO on looking in the other direction. 1q211 microdeletion syndrome is a chromosome abnormality where a segment of genetic material on the long arm or q arm of chromosome 1 at position 211 is missing or deleted.
Typically these types of Bartter Syndrome are identified in infancy or early childhood. Both types of diabetes are chronic diseases that affect the way your body regulates blood sugar or. Research suggests that type 1 is caused by a mutation in one of.
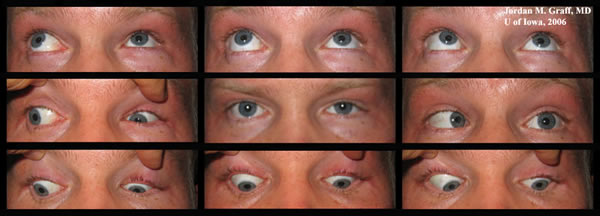
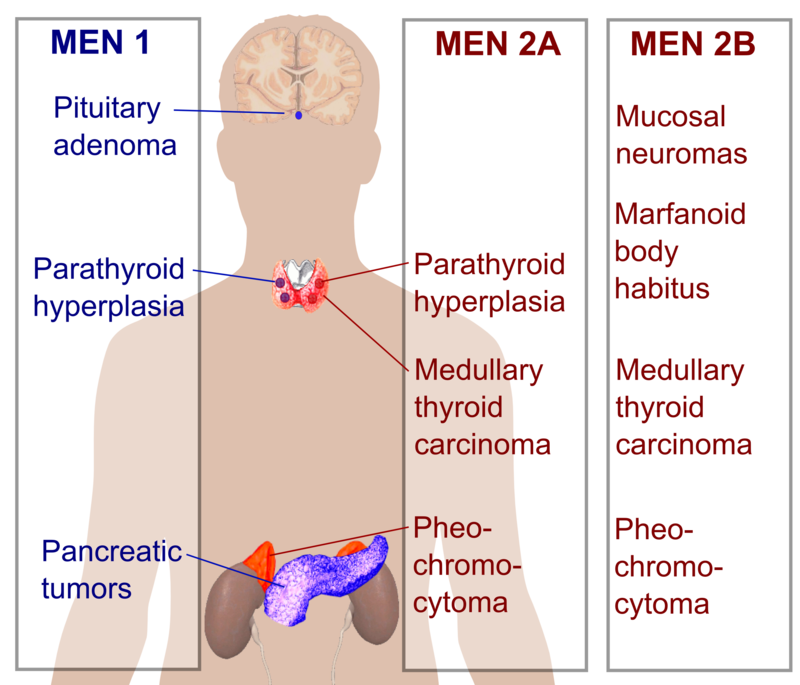
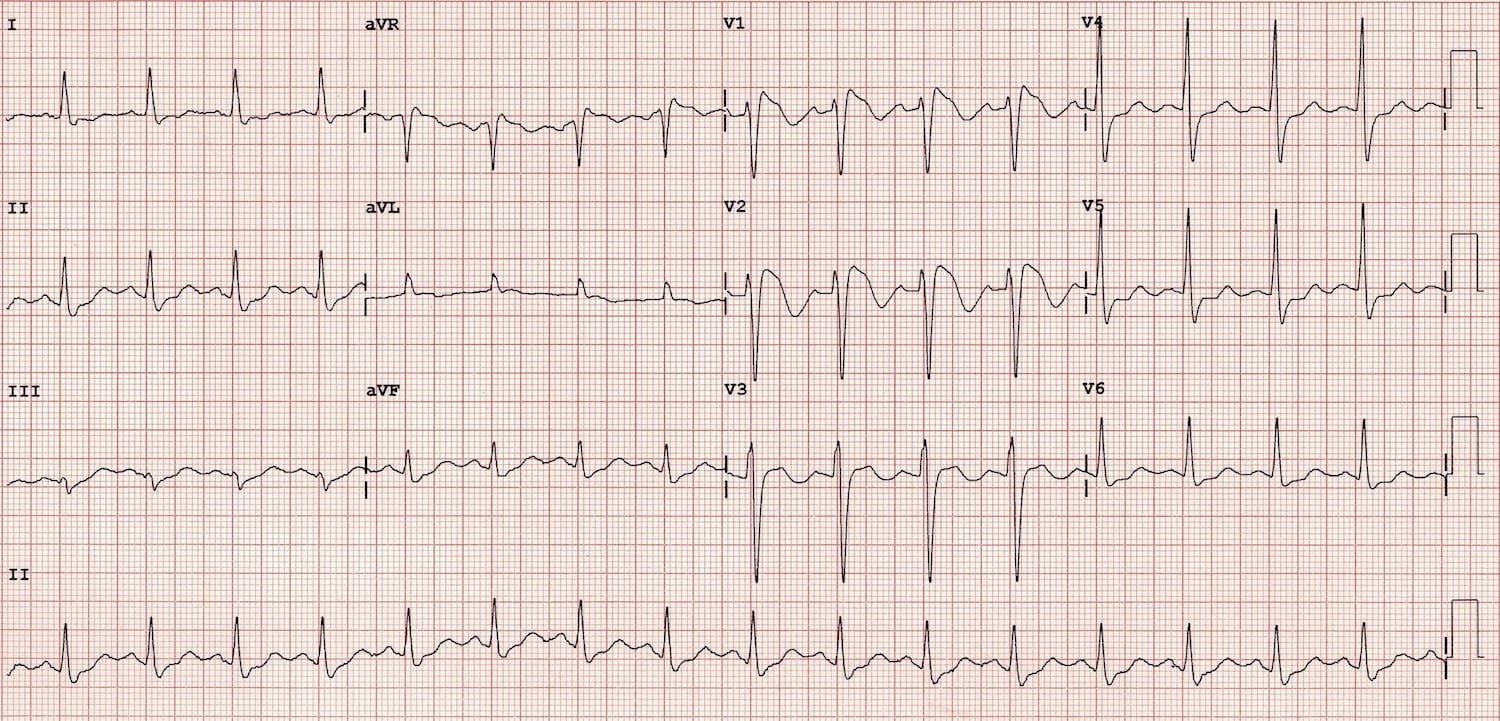
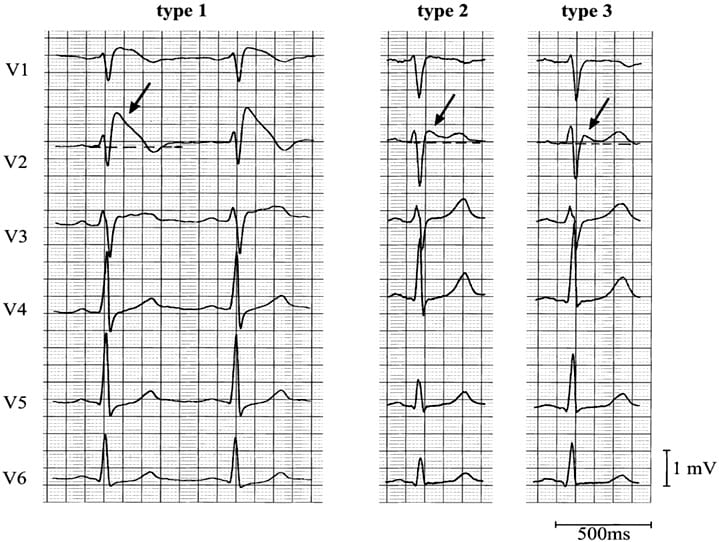
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 MEN-1 is one of a group of disorders the multiple endocrine neoplasias that affect the endocrine system through development of neoplastic lesions in pituitary parathyroid gland and pancreas. The most typical and diagnostic is type 1 Brugada syndrome. The Brugada syndrome may present with three different ECG patterns referred to as type 1 type 2 and type 2 Brugada syndrome ECG.
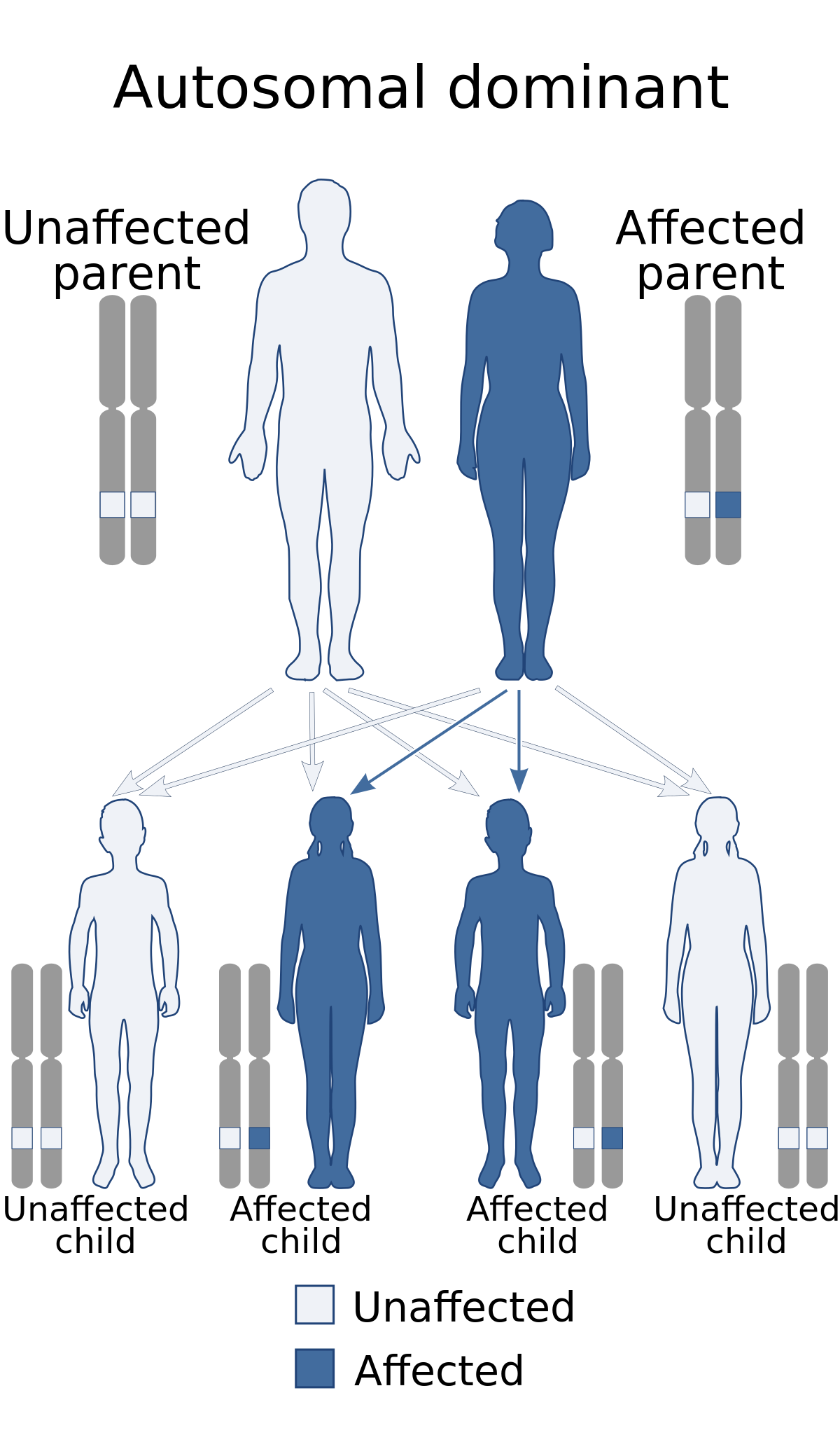
In about 1 in 10 cases the mutation is not inherited from either parent but develops on its own. Type 1 and type 2. 1q211 microduplication is a chromosomal change in which a small amount of genetic material on chromosome 1 is abnormally copied duplicated.
Some people with this deletion have no observable features while others have variable findings that can include a small head microcephaly developmental delay speech and motor delays mild intellectual. Some people with a 1q211 microduplication have developmental delay and intellectual disability that is typically mild to moderate. If one parent has the MEN1 gene each child has a 1 in 2 50 chance of having the disorder.
The coved ST-segment elevations may resemble a shark tale. It features large coved ST-segment elevations and T-wave inversions in leads V1V3.
The coved ST-segment elevations may resemble a shark tale.
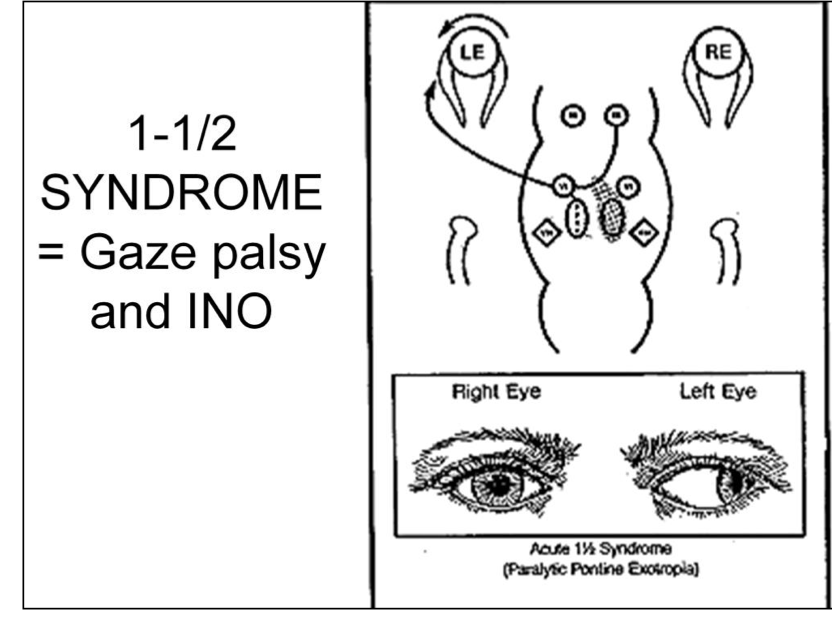
Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 MEN-1 is one of a group of disorders the multiple endocrine neoplasias that affect the endocrine system through development of neoplastic lesions in pituitary parathyroid gland and pancreas. 31 What is one-and-a-half syndrome. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 MEN-1 is one of a group of disorders the multiple endocrine neoplasias that affect the endocrine system through development of neoplastic lesions in pituitary parathyroid gland and pancreas. The most typical and diagnostic is type 1 Brugada syndrome. Boys and girls are affected equally. Magnetic resonance imaging in cases 1 and 2 was unremarkable whereas magnetic resonance angiography demonstrated pathophysiologically significant vertebral basilar disease. Three cases of isolated one-and-a-half syndrome with facial nerve palsy related to infarction are presented. Case 3 is unique due to its association with giant cell arteritis. The only remaining horizontal movement is contralateral abduction.
The apparent adduction deficits can be overcome with convergence. Three cases of isolated one-and-a-half syndrome with facial nerve palsy related to infarction are presented. Type 1 and type 2. One and a Half Syndrome. Research suggests that type 1 is caused by a mutation in one of. If one parent has the MEN1 gene each child has a 1 in 2 50 chance of having the disorder. The duplication occurs on the long q arm of the chromosome at a location designated q211.






























Posting Komentar untuk "1 1/2 Syndrome"