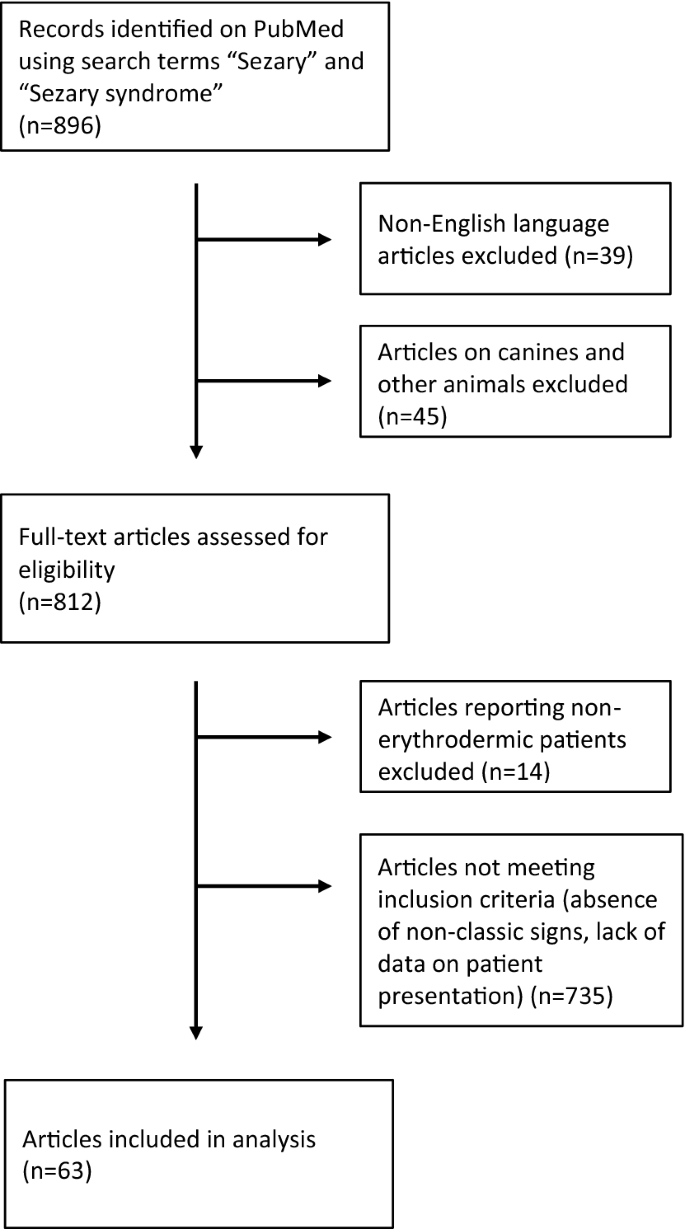
Sezary Syndrome Diagnostic Criteria
Sezary syndrome diagnostic criteria. Therapies include photopheresis with or without interferon chemotherapy and total skin electron beam therapy. Evaluation criteria were i epidermal and dermal changes. Peripheral blood is involved morphologically by cerebriform lymphocytes that by flow cytometry express CD3 CD4 and lack CD7 and CD26.
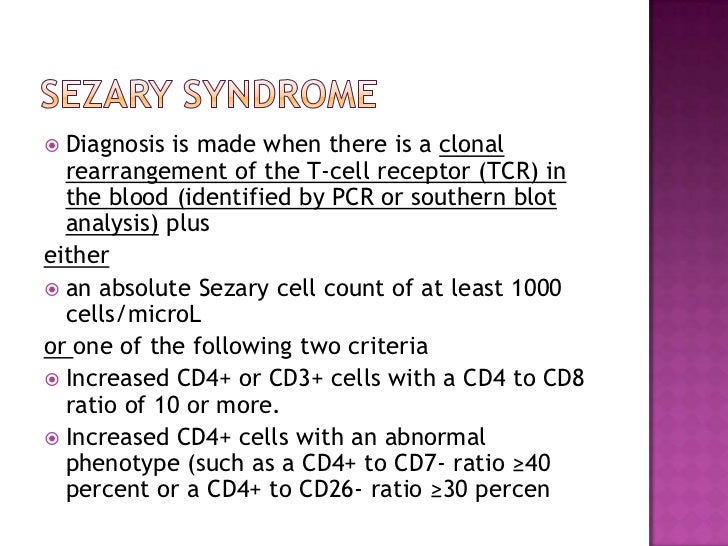
As loss of these markers is not completely sensitive or specific for Sezary cells and there are circulating normal CD4-positive T-cells which usually cannot be excluded from the analysis the WHOEuropean Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer EORTC classification of skin tumors proposed cutoffs of 30 for CD26 loss and 40 for CD7 loss on CD4-positive T-cells as diagnostic criteria for. Sézary syndrome SS is defined as erythroderma plus evidence of malignant circulating T cells that satisfy any of the five criteria listed in Table 79-3. Mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome are types of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
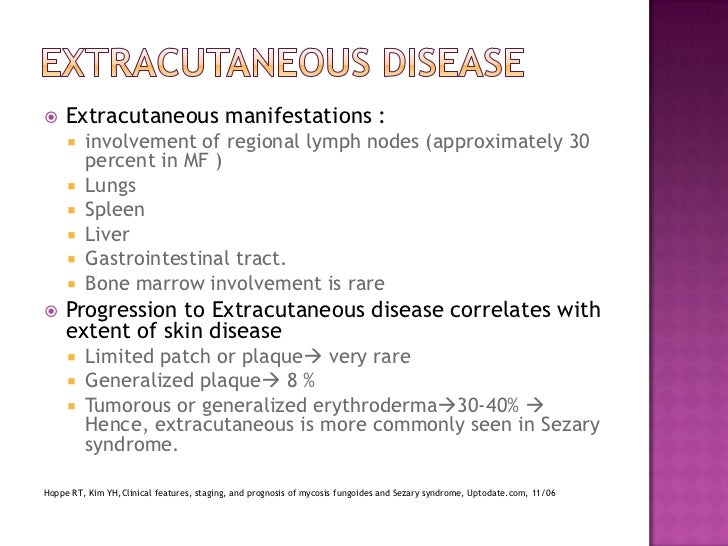
Iv bystander infiltrate by staining for CD8 FOXP3 and CD25. Iii immunohistochemical analysis of marker loss CD2 CD3 CD4 CD5 and CD7. MF is a mature T cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma with presentation in the skin but lymph nodes blood and viscera may also be involved 2.
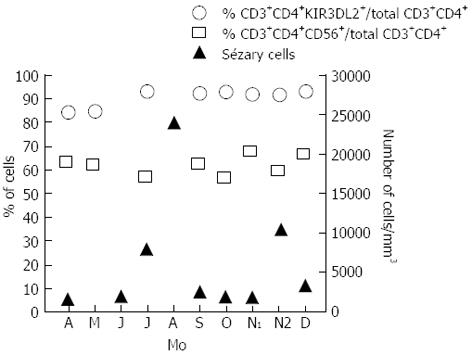
Sezary syndrome is a leukemic form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma CTCL. It is characterized by exfoliative erythroderma peripheral adenopathies and circulating atypical lymphoid cells. Sézary syndrome SS is a rare form of erythrodermic cutaneous T-cell lymphoma with hematological involvement and a poor prognosis.
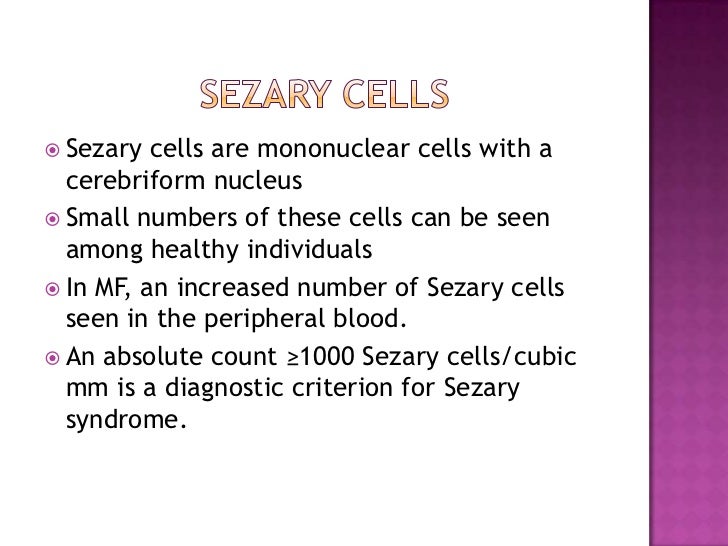
By definition it is associated with systemic skin involvement erythroderma and the presence of at least 1000mcL of circulating cells with irregular nuclear features Sezary cells. The lack of any randomized studies makes it difficult to assess the effect of current therapy on survival. 60 For the purposes of these criteria the Sézary cell is defined as any atypical lymphocyte with a moderately to.
Diagnosis A skin biopsy A complete blood count Peripheral blood smear Immunophenotyping T- cell receptor TCR gene rearrangement test Flow cytometry. Sézary syndrome SS and mycosis fungoides MF are the most common subtypes of cutaneous T cell lymphoma CTCL 1. In Sézary syndrome cancerous T-cells are found in the blood.
49 At a minimum. In patients with erythroderma criteria recommended for the diagnosis of SS by the ISCL include the following.
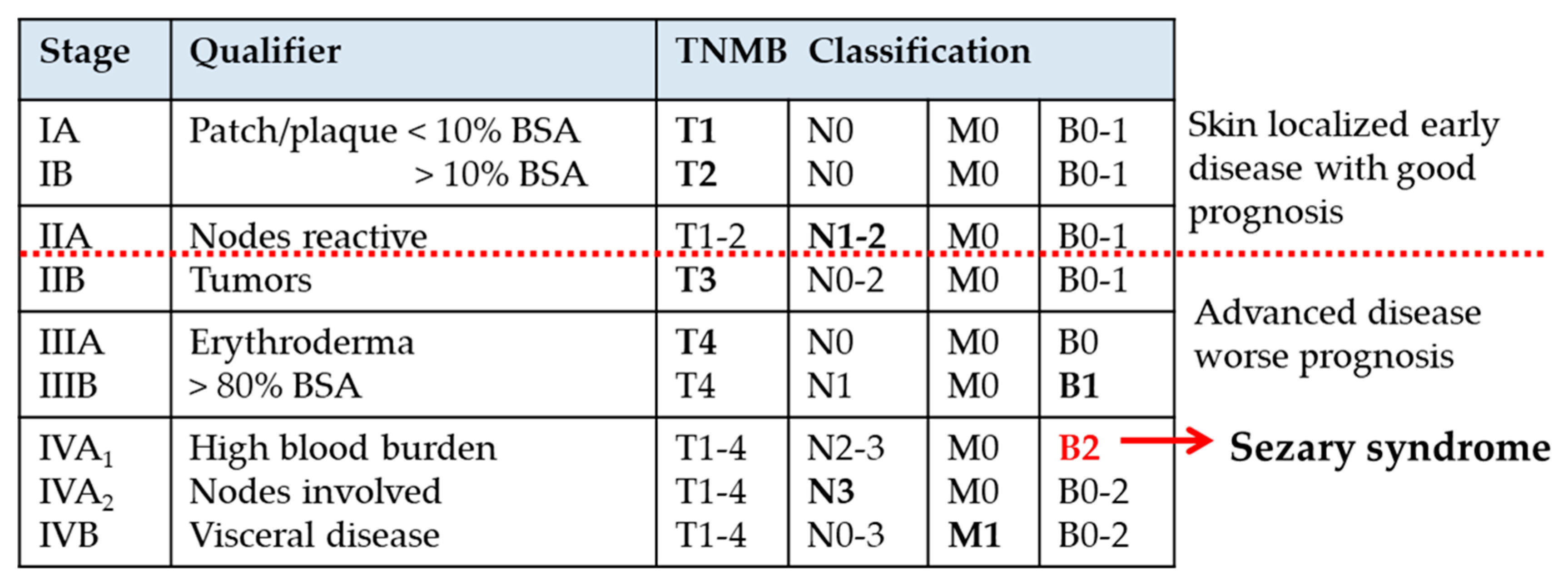
TNMB criteria for staging CTCL are skin T lymph node N visceral involvement M blood B.
These features support the diagnosis of Sézary syndrome. Mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome are types of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Sezary syndrome is a leukemic form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma CTCL. It is often difficult to make a clinical or histologic diagnosis of erythrodermic mycosis fungoides MF and Sezary syndrome SS. Diagnosis A skin biopsy A complete blood count Peripheral blood smear Immunophenotyping T- cell receptor TCR gene rearrangement test Flow cytometry. MF is a mature T cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma with presentation in the skin but lymph nodes blood and viscera may also be involved 2. Iii immunohistochemical analysis of marker loss CD2 CD3 CD4 CD5 and CD7. By definition it is associated with systemic skin involvement erythroderma and the presence of at least 1000mcL of circulating cells with irregular nuclear features Sezary cells. Sézary syndrome SS is a rare form of erythrodermic cutaneous T-cell lymphoma with hematological involvement and a poor prognosis.
49 At a minimum. In summary patient presented with erythroderma and skin is involved by cerebriform T lymphocytes with minimal epidermotropism. Discriminating criteria between Sézary syndrome and benign diseases were sought. It is characterized by exfoliative erythroderma peripheral adenopathies and circulating atypical lymphoid cells. As loss of these markers is not completely sensitive or specific for Sezary cells and there are circulating normal CD4-positive T-cells which usually cannot be excluded from the analysis the WHOEuropean Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer EORTC classification of skin tumors proposed cutoffs of 30 for CD26 loss and 40 for CD7 loss on CD4-positive T-cells as diagnostic criteria for. 60 For the purposes of these criteria the Sézary cell is defined as any atypical lymphocyte with a moderately to. Ii morphology of the infiltrate.


























Posting Komentar untuk "Sezary Syndrome Diagnostic Criteria"